Medical Eye Concerns
Learn More About Your Area of Concern
Allergies? Dry Eyes? Watery Eyes?
Dr. Oevermann can help! As a therapeutic optometrist, he can prescribe topical antibiotics and steroids for a wide variety of eye diseases and infections.
Causes
Cataracts occur when the natural lens inside the eye becomes discolored or cloudy, causing blurred or distorted vision. This blurring is the result of a chemical change within the eye, most often occurring after the age of 55. The direct cause of cataracts is not known, although heredity, injury, and/or disease might be factors. Additional factors that may contribute to the development of cataracts include exposure to ultraviolet light, smoking, and certain prescription drugs.

Symptoms
Indications that cataracts may be forming include:
- blurred/hazy vision
- spots in front of the eyes
- increased sensitivity to light and resulting glare
- feeling of “film” over the eyes
- a temporary improvement in near vision
- decreased vision in low illumination (night driving)
Diagnosis and Treatment
Although there is currently no known method to keep cataracts from developing, Dr. Oevermann can diagnose and monitor cataracts, and also prescribe glasses or lenses that may improve your vision. Ultimately, most cataracts should be surgically removed. Dr. Oevermann can co-manage your cataract surgery with Slade & Baker.
For additional information on cataracts visit the American Optometric Association and Eye Center of Texas websites.
The clear, protective “window” at the front of your eye is called the “cornea.” The most common types of eye injuries involve the cornea. A corneal abrasion is a superficial scratch to the cornea. Don’t let the “superficial” term fool you, corneal abrasions can be painful. If you have ever experienced a scratch to your eye, you can attest to this!
In case of a corneal abrasion, seek medical attention promptly. Some corneal abrasions can become infected and result in a corneal ulcer, which is a serious complication. Corneal abrasions can be caused by contact with dust, dirt, sand, wood shavings, metal particles and even the edge of a piece of paper. Plant matter (tree branches, pine needles, etc.) can sometimes cause a delayed inflammation inside the eye

How can you tell if you have a corneal abrasion?
- Feel like you have sand in your eye
- Excessive tears
- Blurred vision
- Increased sensitivity
- Redness around the eye
Steps YOU CAN take before seeing Dr. Oevermann
- Blink multiple times. This action may remove small particles of dirt or dust.
- Rinse your eye with clean water or saline solution. Rinsing your eye may remove the irritant.
- Pull the upper eyelid over the bottom lid. Your lashes on the lower eyelid can brush the irritant from the under surface of your upper eyelid.
Steps to AVOID before seeing Dr. Oevermann
- Don’t rub your eye after an injury: Pressing or touching your eye after a corneal abrasion can make the injury worse.
- Don’t try to remove the object if it is embedded in your eye. Do not try to remove a large object that makes closing your eye difficult. Removal of the object should be done by Dr. Oevermann.
- Don’t touch your eyeball with tweezers, cotton swabs or other instruments.
If you feel like there is something in your eye, blink a few times and see if it will come out. Sometimes small particles (like eyelashes, dust, etc.) can feel larger than they are and irritate the eye.
However, sometimes foreign bodies can be lodged in the eye tissue. In this instance, you should never try to remove the object.
Foreign body lodged in patient’s eye
The foreign object could be imbedded in the delicate tissues of the eye, and removal at home could cause serious injury to your eye. Dr. Oevermann uses specialized tools to perform this procedure.
Safety Tip!
When participating in activities such as cutting wood or grinding metal, wear safety glasses to prevent this type of injury.
These activities can create projectile objects that could fly into your eyes at a very high rate of speed. Safety glasses are a must in these situations.
Call our office at 281-550-4141 for additional details.
Causes
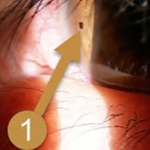
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the U.S. It typically affects people over the age of 40. The early signs may occur when the passages that filter and exchange fluid from within the eye become blocked, causing the internal eye pressure to increase.
Undiagnosed and untreated, this increased pressure may cause permanent damage to the optic nerve.
The chances of developing glaucoma are increased when there is a family history of the disease, or when an individual is of African descent, very nearsighted, or has diabetes.
Symptoms
Glaucoma tends to develop gradually and without symptoms. If there are symptoms, they may include the following:
- minor blurring of vision
- loss of central or peripheral vision
- the appearance of colored rings around lights
- eye pain or dull headaches
Diagnosis and treatment
Glaucoma cannot be prevented, but it can, in most cases, be controlled. A comprehensive eye exam can detect the onset of signs and symptoms of glaucoma.
Dr. Oevermann will do further testing and may prescribe medication to control the pressure inside the eye or recommend other forms of treatment, including laser or conventional surgery.
LASIK (Laser In-situ Keratomileusis) is currently the most technologically advanced refractive surgical procedure to reduce or eliminate near-sightedness, far-sightedness, and astigmatism. The procedure involves reshaping the cornea with an extremely precise laser so that light entering the eye is correctly focused. Dr. Oevermann works with several LASIK surgeons and can assist each patient in choosing the best surgeon. All pre-operative and post-operative care is conveniently performed in our office.
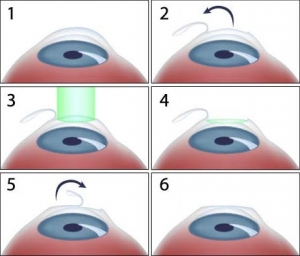
Coordinated care through Cypress Family Eyecare and Slade & Baker Vision Center – from $4,200. For additional information, please call our office at 281-550-4141 or email us at dro@cfeyecare.com.

Visit the Slade & Baker Vision Center website to learn more.
Macular Degeneration is the leading cause of blindness in the United States
Causes
In Macular Degeneration, the macula (i.e., the part of the retina responsible for clear central vision) undergoes vascular changes that may cause loss of central vision.
This condition is usually permanent and may progress if it goes undetected and untreated.
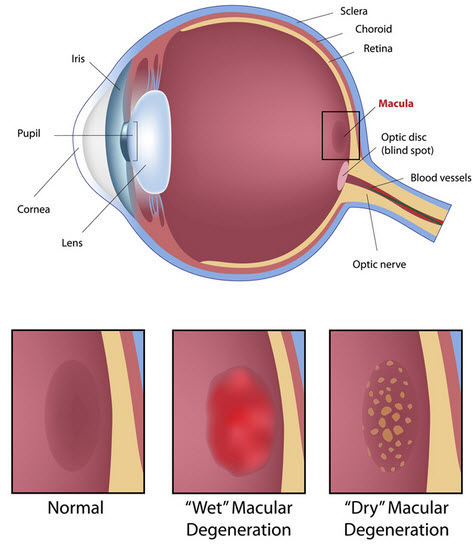
Macular Degeneration
Symptoms
The symptoms of Macular Degeneration include:
- gradual loss of clear central, or “straight-ahead” vision
- distorted or wavy vision
- gradual loss of color vision
- a dark or empty area (i.e., “blind spot”) in the center of your field of vision
Diagnosis and Treatment
The more common form of Macular Degeneration is the dry form. Unfortunately, there is no known treatment for this form. A less common form of Macular Degeneration is the wet form, in which fluid leaks from blood vessels surrounding the macula. If detected early, this form may be treatable with certain laser procedures.
Although central vision loss cannot be restored, special optical devices can be prescribed to help maximize the effectiveness of remaining vision. In addition, certain vitamin and mineral supplements may help prevent or slow the progression of Macular Degeneration.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the eyelids is a condition called Blepharitis. This can be a chronic condition that is difficult to treat. Typically, the inflammation occurs on the eyelid margins where the eyelashes grow.

Ocular Infections & Inflammation
Blepharitis is a common condition caused by a malfunction of the oil glands at the base of the eyelashes. Such a malfunction can cause the growth of bacteria, which can then irritate and inflame the eyelids.
Symptoms may include the following:
- Itchy eyelid
- Red and swollen eyelid
- Scaly, greasy debris along eyelid margin
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, contact Dr. Oevermann at 281-550-4141.
Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva is the clear mucous membrane that covers the white part of your eye. The main function of the conjunctiva is to help lubricate the eye by producing mucus and tears.
Conjunctivitis is a common form of ocular infection in which the conjunctiva becomes inflamed or irritated. Conjunctivitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, allergies, or chemical irritants.
There are many forms of conjunctivitis, and symptoms include itchy, burning or teary eyes. With the exception of conjunctivitis caused by allergic and chemical irritants, conjunctivitis caused by bacterial and viral sources is extremely contagious. Since the symptoms are similar, only your doctor can distinguish between them. Making an appointment with Dr. Oevermann at the first signs of conjunctivitis will ensure that you receive proper care and treatment.
One of the most common types of conjunctivitis is “pink eye” and it is often caused by bacteria such as staphylococcus and streptococcus. Bacterial conjunctivitis can occur in otherwise healthy individuals and symptoms may include the following:
- Thick, white or creamy discharge
- Swollen , itchy eyelid
- Redness
- Tearing
- Gritty feeling in eye
- Usually affects only one eye, but can spread very easily to the other eye.
Many of our patients take hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) as treatment for lupus, rheumatoid arthritis or other systemic conditions. One concern for these patients is retinal toxicity, which is known to occur with such treatment. Interval monitoring is aimed at early detection rather than prevention.
Many symptoms or early warnings go unnoticed or are lacking altogether. Some patients, however, may notice a blurred area near the center of their vision. Unfortunately, once this blurred vision is noticed, discontinued use of the drug is not likely to improve the vision level.
Dr. Oevermann will examine patients on a regular basis depending on the dosage level of Plaquenil. Re-evaluations will take place annually or every six months depending on the risk factors and dosage levels. The standard of care would be as follows:
Our new HD-OCT equipment will allow Dr. Oevermann to monitor any changes in your eye. The 3-D images will allow for a more clinical certainty.
Uveitis is the inflammation of the uvea, which is the layer between the retina and the white of the eye (sclera).
The exact cause of uveitis is often unknown, but it can be caused by infections, injury, and autoimmune disorders.
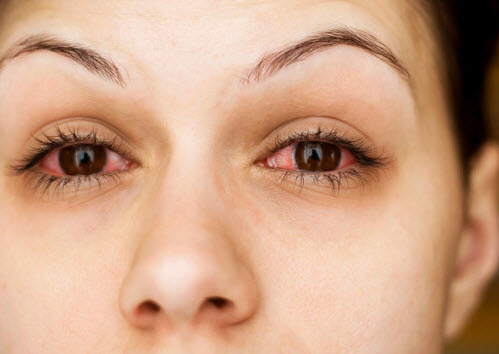
Symptoms
Since the symptoms can vary in their onset (can occur suddenly or develop gradually), it is important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
- Eye redness
- Eye pain
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
- Floaters – dark floating spots in your field of vision
- Decreased vision
- Whitish area inside the lower part of your iris (colored part of the eye)
Complications
Timely diagnosis and treatment is critical to prevent serious complications of uveitis, which can lead to permanent vision loss.
- Damage to the optic nerve
- Glaucoma – unusually high pressure inside the eye
- Retinal problems – retinal detachment or fluid within the retina
- Cataract – clouding of the lens
- Cornea
- Vision loss
A complete exam would be recommended in order to diagnose this condition. Contact Dr. Oevermann at 281-550-4141 if you are experiencing any of these symptoms.

